New photo raises concerns about the health of NASA astronaut Sunita Williams
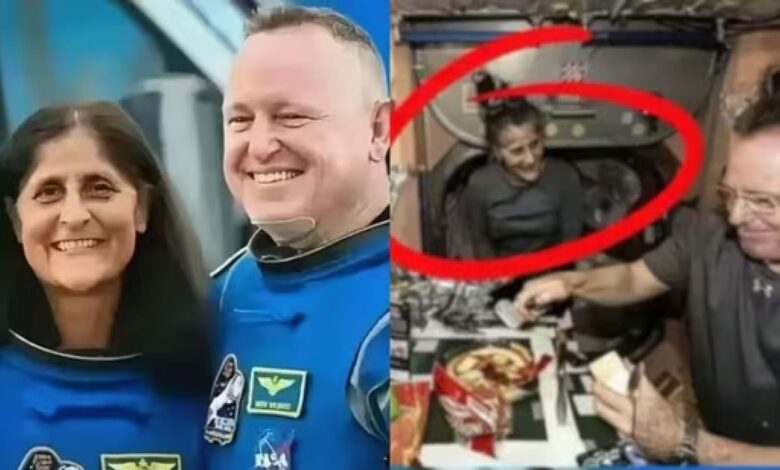

Concerns about astronaut Sunita Williams’ health have surfaced after a recent photo showed her looking visibly thin following her extended mission on the International Space Station (ISS). Williams, 59, and fellow astronaut Barry Wilmore were initially scheduled for an eight-day mission aboard Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft. However, due to a malfunction, they have been stranded on the ISS since their docking on June 6, while Williams has now been in orbit for more than 150 days.
Health implications of extended space missions
According to one report by DailyMail Dr. Vinay Gupta, a pulmonologist based in Seattle, expressed concern after viewing the recent image, noting signs of significant weight loss. He explained that the body burns more calories in space as it adapts to unique conditions, requiring astronauts to eat a high-calorie diet. Calorie intake alone may not be enough, as Dr. Gupta has observed indications of a possible calorie deficit that could affect Williams’ appearance and well-being.
Space conditions intensify the physiological stress due to factors such as reduced oxygen levels and the body’s increased metabolism in response to cold. To combat muscle and bone loss, ISS crew members engage in approximately 2.5 hours of exercise every day, which can further deplete calorie reserves. Dr. Gupta said that in space your metabolism requires more energy to function, describing the physiological challenges astronauts face.
Differences in health risks between men and women in space
Concerns have been heightened by studies showing that space travel poses different health problems for men and women. Research by NASA has shown that women can experience more pronounced losses in blood plasma and muscle mass than men. A recent study from Ball University observed muscle wasting in both men and women subjected to simulated weightlessness, with women showing greater muscle loss within shorter periods.
These findings underscore the need for tailored health care support for extended space missions, especially for female astronauts. As Williams and Wilmore await a safe return to Earth, NASA is likely keeping a close eye on their health, with the recent hospitalization of another NASA crew after an extended stay on the ISS further amplifying these concerns.