ChatGPT is getting a new web search to tackle Google Search, Perplexity
ChatGPT Search, the artificial intelligence (AI) search engine for the chatbot built by OpenAI, was introduced on Thursday. The feature comes after months of speculation about the AI company’s SearchGPT waitlist. Web search allows users to search the Internet for a topic and get natural language results based on information collected from various websites. This new capability is integrated into the ChatGPT interface and can be activated either manually or automatically. ChatGPT Search is currently being rolled out to paying subscribers of the AI chatbot.
ChatGPT Search Introduced by OpenAI
In one blog postOpenAI has detailed the new web search feature for ChatGPT. Previous reports have highlighted that the AI company was building its own search engine to reduce dependence on third-party search engines. The feature also fills an important gap compared to AI chatbots like Gemini and Copilot, which can perform web searches based on user prompts.
Notably, the GPT-4o AI model had real-time web search capabilities, but there were two caveats. The answers were integrated into the conversation so that users could not distinguish whether the information came from the AI model’s datasets or from the Internet. Second, users had no direct way to trigger a web search.
![]()
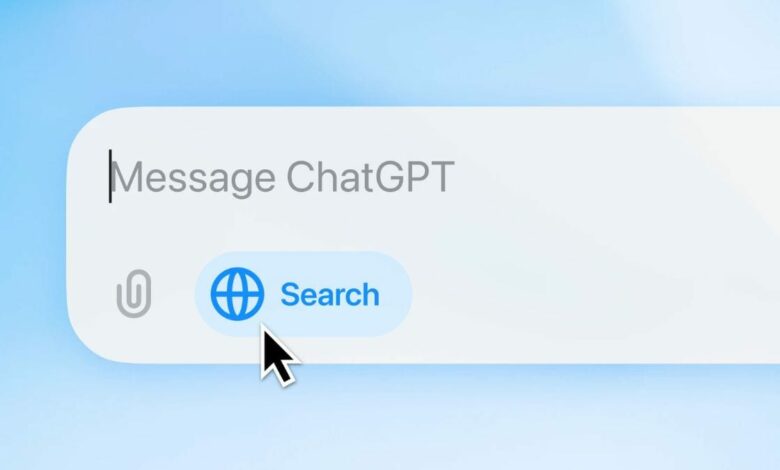
ChatGPT search function
The new ChatGPT search function solves both problems. Users will now see a globe icon next to the ‘Attach file’ icon in the text field. Tapping the globe icon manually activates web search mode, and the chatbot uses only information found on the web to answer user responses. OpenAI said the AI tool will also automatically activate search mode where it is relevant to the search query. With the introduction of ChatGPT Search, OpenAI also competes with Perplexity AI and Google’s AI Overviews.
Gadgets 360 employees were able to test the feature, and the feature is quite fast and responsive. Despite searching multiple websites for a query, it never took more than a few seconds for the output generation process to start. Furthermore, the emphasis is on quotations, as each source is cited twice: once after the end of the sentence in which the information was used, and once at the bottom of the answer.
The latter is a detailed citation where the website headline and article are both shown, while the former is a chip-style citation where only the website name is shown, but users can click on it to go to the source URL.
Currently, ChatGPT Plus and Teams users, as well as those who have signed up for the SearchGPT waitlist, get the web search feature. Enterprise and Edu users will get access to the feature in the coming weeks and those on the free tier will get the feature in the coming months.



