Is Your Skin Suffering From Sun Damage? We Asked Experts If You Can Reverse It
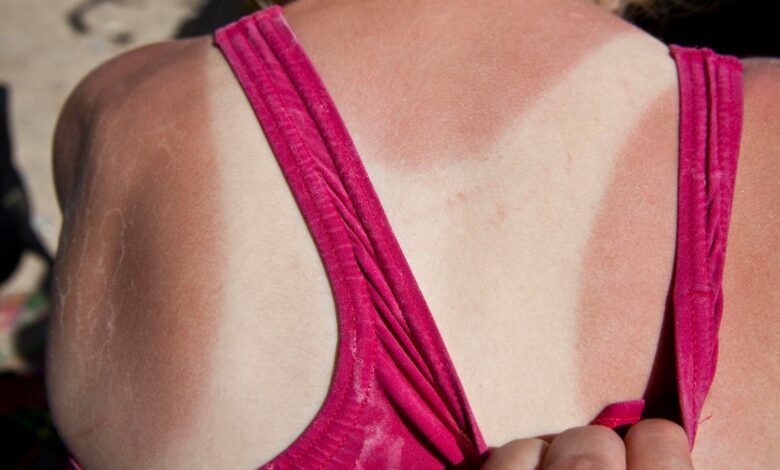


As summer draws to a close, many people are likely noticing changes in their skin — whether it’s a simple tan or more serious sun damage. But aside from getting regular skin cancer screenings and wearing SPF every day (even indoors), what else can you do about sun damage?
Tanning is a common cause of sun damage. The American Academy of Dermatology explains that there is no safe way to tan — All tanning causes skin damage. But is it possible to reverse these effects for those with sun damage on their skin? We spoke to experts to learn more about all things sun damage.
What is sun damage?
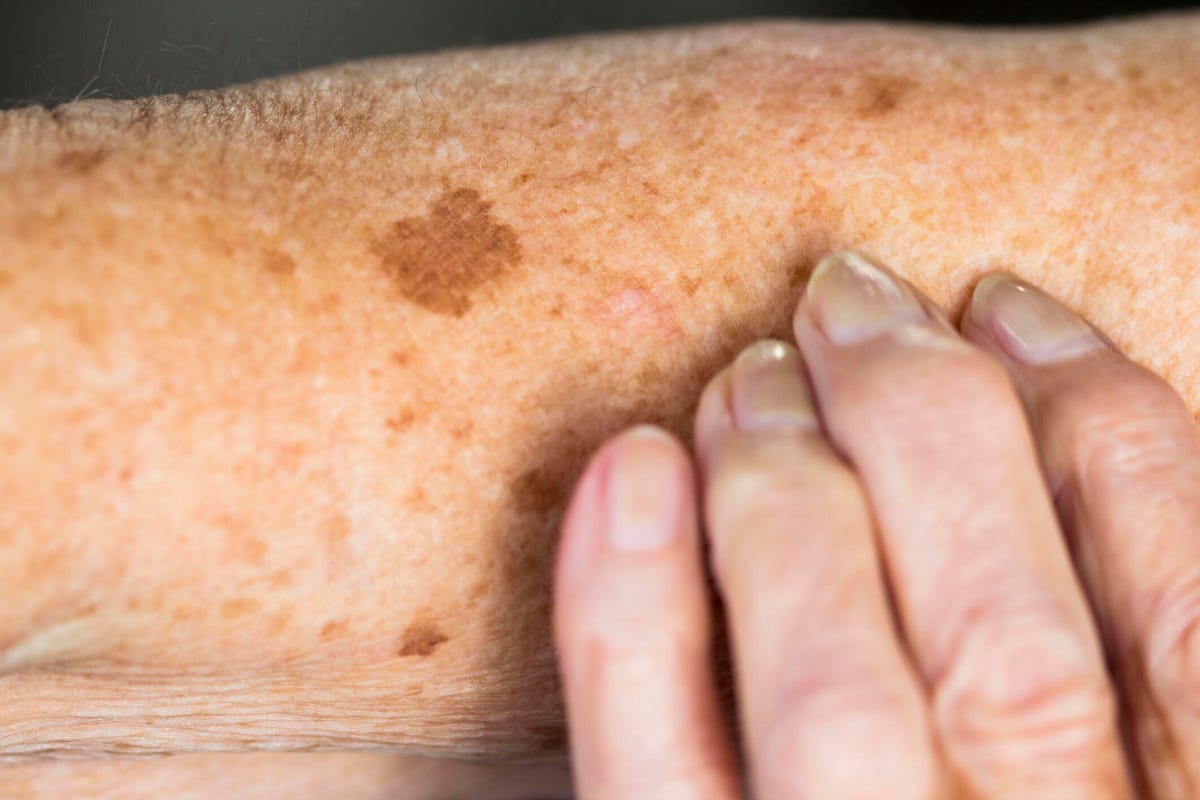
“Sun damage” is a catch-all term that refers to any damage the sun does to your skin. It manifests in a variety of ways, said Dr. Susan Bard, a board-certified dermatologist at Dermatology Specialists in Manhattan.
“Sun damage can show up as dark spots, abnormal blood vessels or redness, or with sagging and wrinkling,” Bard said. “It can also show up as precancerous skin lesions that feel like little scabs on the skin.”
Dr. Hadley King, a board-certified dermatologist in New York City, said sun damage often looks different on different skin tones. “Lighter skin tones will show thinning, fine lines and discoloration,” she said. “In darker skin tones, discoloration may be the most noticeable sign of sun damage.”
The technical term for these changes is “photoaging.” While most people know photoaging as the result of sun damage, other types of damage can occur, depending on the type of UV radiation penetrating the skin.
“UVA rays are generally associated with aging of skin cells and are often the cause of wrinkles, sun spots and other signs of sun damage,” King said. “UVB rays, on the other hand, are the leading cause of sunburn, directly damage DNA in skin cells and are linked to most forms of skin cancer.”
It is also important to note that everyone is at risk for sun damage and, as a result, skin cancer. All ages, genders, ethnicities and skin colors are at risk for sun damage if exposed.
Can you reverse sun damage?

King and Bard both say that it is possible to partially reverse — or a better word is “treat” — some types of sun damage. If you have discoloration, wrinkles, fine lines or other signs of photoaging, a dermatologist can help you address those types of sun damage.
“It is possible to turn back [sun damage] “To some extent, using lasers, chemical peels and certain topical medications to destroy dark spots and blood vessels, stimulate collagen deposition and remove the damaged layers of skin,” Bard said. She clarified that combining multiple treatments is usually necessary to address the different components of sun damage.
Certain at-home treatments can also help. King said humectants and emollients can hydrate and smooth the skin so it looks plump, which is especially important for dry skin. Anti-aging topicals, such as retinoids, antioxidants, peptides and alpha hydroxy acids, can also help, King said.
Topical retinoids are the most proven anti-aging topical option, she said. These compounds are “very powerful and capable of making significant changes in the skin. They increase skin cell turnover, increase collagen production and reduce discoloration,” and also reduce pore clogging, King said.
Your dermatologist can help you choose a treatment tailored to your specific needs.
But don’t get too excited
While you can treat the aesthetic effects of sun damage, unfortunately, you can’t reduce or reverse the DNA damage caused by the sun, Bard says. “Once DNA mutation has occurred from UV exposure, there’s no way to reverse it. The cell has to be destroyed by an external modality or by the body,” she explains.
UV radiation is a known human carcinogen, King said. According to the Skin Cancer Foundationdoubles your risk of melanoma if you’ve been sunburned more than five times. Just one blistering sunburn in childhood or your teens can more than double your risk of developing this deadly skin cancer later in life.
How do you prevent sun damage?

Prevention is key to preventing sun damage from both UVA and UVB rays. Daily protection is crucial, King said, because “much of the sun damage that accumulates in our skin is a result of incidental exposure to the sun every day.”
King quoted an Australian study that followed the skin of people who wore sunscreen every day, regardless of the weather or their daily activities. The researchers compared this to the skin of people who only wore sunscreen on particularly sunny days or when they thought they would spend a lot of time outside. The results? The skin of the people who wore sunscreen every day aged significantly better.
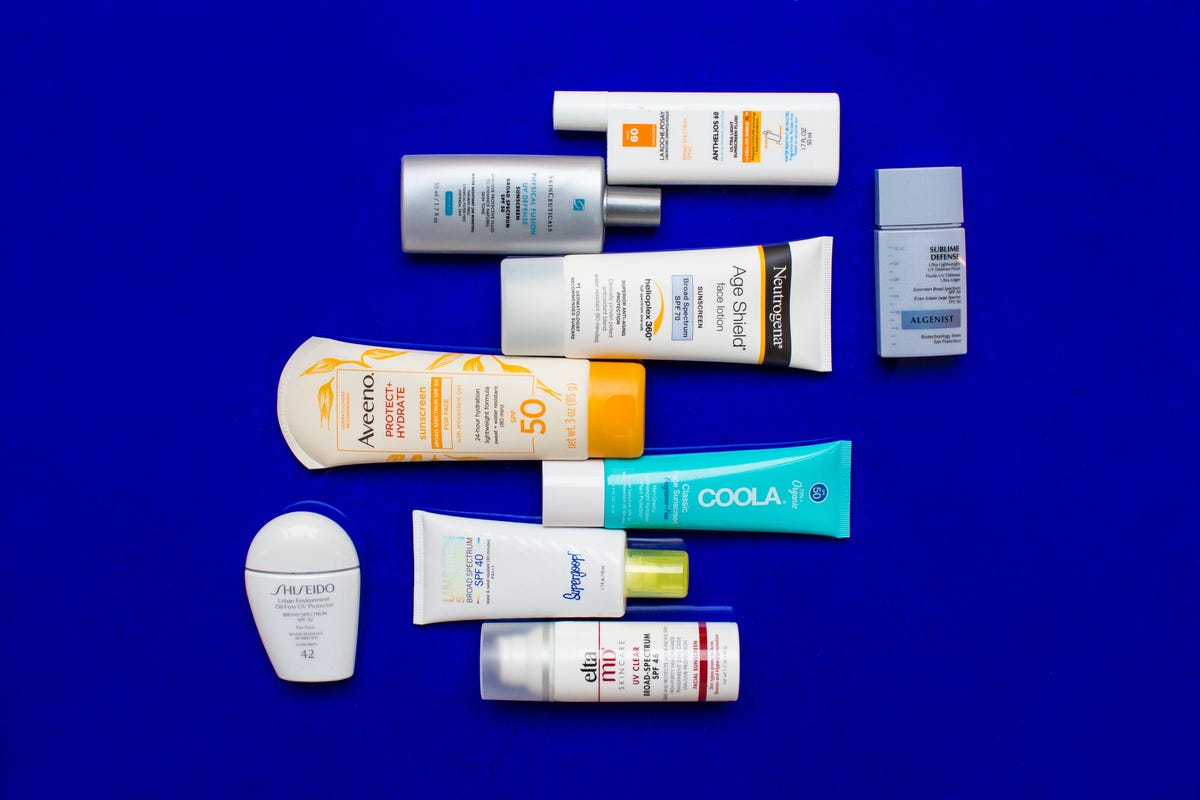
That’s why you need sunscreen that minimum SPF 30. Make sure to apply this to exposed skin and reapply according to the instructions on the package. Even on a cloudy day, you should still wear sunscreen, as clouds do not protect against skin damage and UV rays can still penetrate. To further protect yourself, you can also wear wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and clothing that covers and protects your skin.

Don’t wait until you see signs of sun damage to take care of your skin. Protecting yourself from UV rays is the best way to keep your skin young and healthy.
Read more: 10 Sunscreen Myths You Should Stop Believing This Summer
Tips to protect your skin from the sun
King and Bard offer the following skin care tips for sun protection:
- Wear sunscreen on any skin that will be exposed to direct sunlight — not just when you’re going to the beach. Daily SPF is essential.
- Wear a hat and sunglasses to protect your eyes and face.
- Seek shade or shelter when the sun is shining brightly.
- Try to avoid direct sunlight during peak hours (this varies by location, but is usually in the afternoon).
- If possible, wear light, breathable, long-sleeved shirts and pants, especially if you are particularly susceptible to sunburn.