Meet Homo juluensis: a newly discovered ancient human species
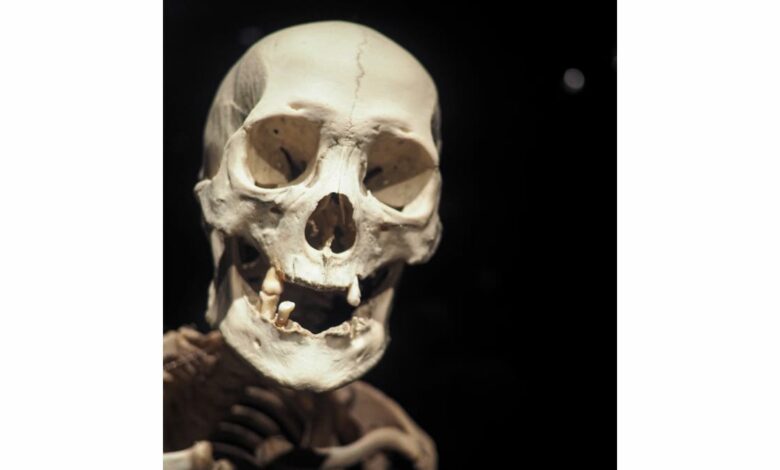
A new ancient human species, Homo juluensis, has been identified by researchers, marking an important step in understanding human evolution in the Middle Pleistocene. According to findings published in PaleoAnthropology in May 2024, the discovery is based on fossil evidence unearthed in China, with specimens dating between 220,000 and 100,000 years ago. The species, known as ‘big-headed humans’, is characterized by large skulls, which combine features of modern humans, Neanderthals and Denisovans.
Fossil evidence and characteristics
The fossils that form the basis for this new classification have been reported to have been recovered from sites in Xujiayao and Xuchang in northern and central China. Excavations at Xujiayao in the 1970s yielded more than 10,000 stone tools and 21 fossil fragments, representing at least 10 individuals. These fossils show large, broad skulls with Neanderthal-like features, but also share traits with modern humans and Denisovans. Four additional ancient skulls discovered in Xuchang show similar characteristics.
The research The team led by Christopher Bae, an anthropologist at the University of Hawaii, and Xiujie Wu, a paleoanthropologist at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, concluded that these fossils represent a separate hominin population. The findings indicate a likely continuity of hybridization among Middle Pleistocene hominids, which shaped human evolution in East Asia.
Naming and expert perspectives
In a statement to Nature Communications published in November 2024, the researchers advocated using Homo juluensis to clarify the complex fossil record of East Asia. Although some experts, such as Chris Stringer of the Natural History Museum in London, have suggested that the fossils may be more closely linked to Homo longi, the designation Homo juluensis has gained popularity.
According to Bae in a statement, the name was introduced to improve scientific communication. Paleoanthropologist John Hawks of the University of Wisconsin-Madison noted in a blog post that such terminology allows for clearer reference to this population’s place in the human evolutionary story. The discovery underlines the complicated relationships within ancient hominin groups and their evolutionary significance.
For the latest tech news and reviews, follow Gadgets 360 X, Facebook, WhatsApp, Wires And Google News. For the latest videos on gadgets and technology, subscribe to our YouTube channel. If you want to know everything about top influencers, follow our in-house Who is that360 on Instagram And YouTube.

Polar bears in Alaska face increasing threats from pathogens due to climate change